


Next: Mechanical Structure
Up: Silicon Vertex Detector, SVD
Previous: General Characteristics
Contents
We use S6936 DSSDs fabricated by Hamamatsu Photonics (HPK). These
detectors were originally developed for the DELPHI micro-vertex
detector [19]. Each DSSD consists of 1280 sense strips
and 640 readout pads on opposite sides. The sense strips are biased
via 25 M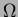 polysilicon bias resistors. The
polysilicon bias resistors. The 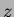 -strip pitch is
42
-strip pitch is
42 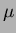 m and the
m and the 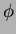 -strip pitch is 25
-strip pitch is 25 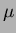 m. The size of the
active region is
m. The size of the
active region is
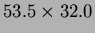 mm
mm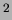 on the
on the 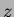 -side and
-side and
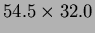 mm
mm on the
on the 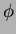 -side. The overall DSSD size is
-side. The overall DSSD size is
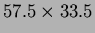 mm
mm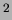 . In total 102 DSSDs are used.
For the
. In total 102 DSSDs are used.
For the 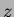 -coordinate (
-coordinate (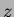 is the approximate beam direction)
measurement, a double-metal structure running parallel to
is the approximate beam direction)
measurement, a double-metal structure running parallel to 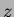 is
employed to route the signals from orthogonal
is
employed to route the signals from orthogonal 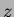 -sense strips to the
ends of the detector. Adjacent strips are connected to a single
readout trace on the second metal layer which gives an effective strip
pitch of 84
-sense strips to the
ends of the detector. Adjacent strips are connected to a single
readout trace on the second metal layer which gives an effective strip
pitch of 84 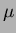 m. The ohmic side is chosen to be on the
m. The ohmic side is chosen to be on the 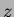 -side
and a
-side
and a 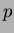 -stop structure is employed to isolate the sense strips. A
relatively large thermal noise (600 e
-stop structure is employed to isolate the sense strips. A
relatively large thermal noise (600 e ) is observed due to the
common-
) is observed due to the
common-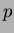 -stop design.
On the
-stop design.
On the 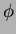 side, only every other sense-strip is connected to a
readout channel. Charge collected by the floating strips in between
is read from adjacent strips by means of capacitive charge division.
side, only every other sense-strip is connected to a
readout channel. Charge collected by the floating strips in between
is read from adjacent strips by means of capacitive charge division.



Next: Mechanical Structure
Up: Silicon Vertex Detector, SVD
Previous: General Characteristics
Contents
Samo Stanic
2001-06-02