


Next: Muon detection
Up: Performance
Previous: Performance
Contents
In order to identify 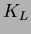 , a cluster must be observed in KLM. Then,
tracks of charged particles measured in CDC are extrapolated into KLM.
Clusters within 15 degrees of an extrapolated charged particle track
are excluded from
, a cluster must be observed in KLM. Then,
tracks of charged particles measured in CDC are extrapolated into KLM.
Clusters within 15 degrees of an extrapolated charged particle track
are excluded from 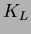 cluster candidates. For an isolated cluster,
the center of gravity of the hits is calculated and used to determine
the direction of the cluster from the interaction point.
Fig.
cluster candidates. For an isolated cluster,
the center of gravity of the hits is calculated and used to determine
the direction of the cluster from the interaction point.
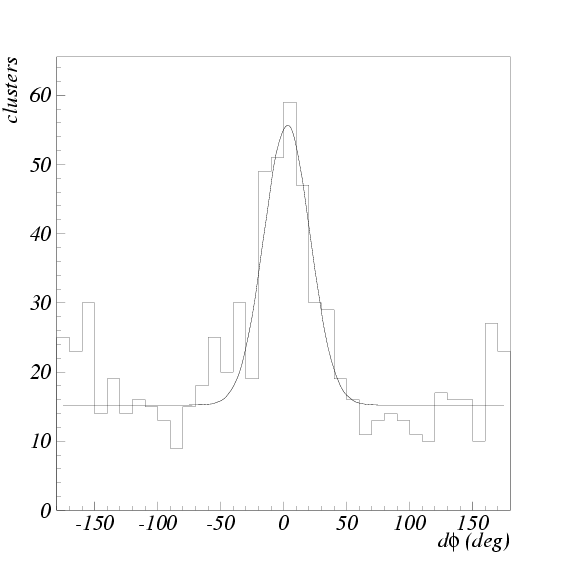
Fig. ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) shows a histogram of the difference between
the direction of the
shows a histogram of the difference between
the direction of the 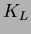 cluster candidate and the missing momentum
direction. The data was obtained during the summer 1999 commissioning
run of the KEK B-factory. The missing momentum vector is calculated
using all the other measured particles in the event. The histogram
shows a clear peak where the direction of the neutral cluster measured
in KLM is consistent with the missing momentum in the event. A large
deviation of the missing momentum direction from the neutral cluster
direction is mainly due to undetected neutrinos and particles escaping
the detector acceptance.
Fig.
cluster candidate and the missing momentum
direction. The data was obtained during the summer 1999 commissioning
run of the KEK B-factory. The missing momentum vector is calculated
using all the other measured particles in the event. The histogram
shows a clear peak where the direction of the neutral cluster measured
in KLM is consistent with the missing momentum in the event. A large
deviation of the missing momentum direction from the neutral cluster
direction is mainly due to undetected neutrinos and particles escaping
the detector acceptance.
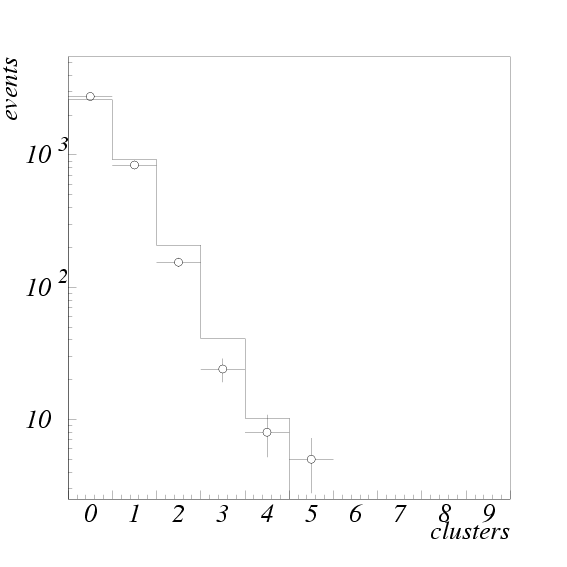
Fig. ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) shows the number of neutral clusters per
event and a Monte Carlo simulation of the predicted number of
shows the number of neutral clusters per
event and a Monte Carlo simulation of the predicted number of 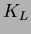 clusters per event. The average number of
clusters per event. The average number of 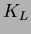 clusters per event is
0.5. The agreement with the prediction gives us the confidence that
the detector and our reconstruction software are performing correctly.
clusters per event is
0.5. The agreement with the prediction gives us the confidence that
the detector and our reconstruction software are performing correctly.
Figure:
Difference between the neutral cluster and the direction of missing momentum in KLM.
|
Figure:
Number of neutral clusters per event in KLM.
|



Next: Muon detection
Up: Performance
Previous: Performance
Contents
Samo Stanic
2001-06-02