


Next: Bibliography
Up: Offline Computing System
Previous: Level 4 Offline Trigger
Contents
The events accepted by the Level 4 software filter are reconstructed
and the information is stored as DST. In this stage, raw data, the
contents of which are direct logs from data acquisition devices, are
converted into physics objects of 4-vectors of and
.
The most downstream of the reconstruction flow is the event
classification and skimming. Here, all events are examined in such a
way that certain selection criteria are applied to select events of
our interest from a large number of background events. Once events are
satisfied with our cuts, they are recorded into not only DST but also
specific data files on the disk as skimmed data. In this way, physics
events such as hadronic events and Bhabha candidates are stored. Based
upon those data, detector calibrations are carried out in detail and
the offline luminosity is computed.
After all information is reconstructed, monitoring modules are called
to keep our data quality reasonably high. Basic observables like the
number of charged tracks reconstructed are booked and those histograms
are checked by experts.
A typical processing speed of DST production, including skimming part,
is around 40 Hz, depending on beam conditions. In our computing
machines, we can process about 80 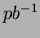 of data a day when three
CPU servers out of seven are allocated. Fig.
of data a day when three
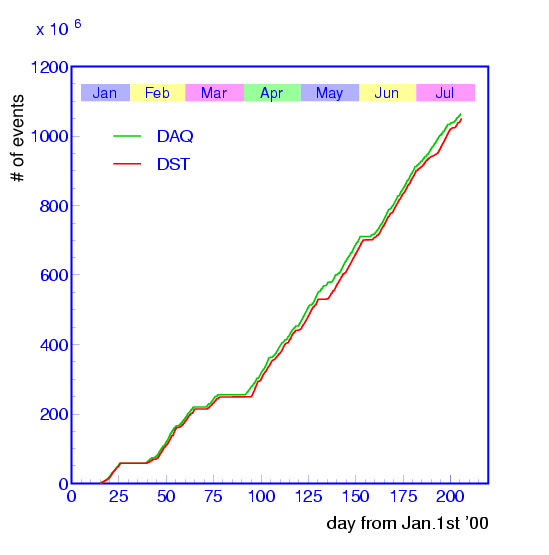
CPU servers out of seven are allocated. Fig. ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) shows
a history of our event processing rate together with the data
acquisition rate in the recent runs. Our offline processing has been
well tracked to the online trigger rate with normally one day delay.
The data size of DST is about 100 KB and 60 KB for hadronic and Bhabha
events, respectively.
The calibration constants, which are used to correct detector
responses, are kept in (www.postgresql) database in our
system. During the period of an experiment, detector raw responses can
be shifted due to changes in environmental conditions. The energy loss
measurements by CDC, for example, suffer from atmospheric pressure
changes. After checking skimmed data created by DST production job,
the detector constants are improved on the weekly basis to correct for
this sort of effects. By getting updated constants, the re-processing
has been made for hadronic events.
shows
a history of our event processing rate together with the data
acquisition rate in the recent runs. Our offline processing has been
well tracked to the online trigger rate with normally one day delay.
The data size of DST is about 100 KB and 60 KB for hadronic and Bhabha
events, respectively.
The calibration constants, which are used to correct detector
responses, are kept in (www.postgresql) database in our
system. During the period of an experiment, detector raw responses can
be shifted due to changes in environmental conditions. The energy loss
measurements by CDC, for example, suffer from atmospheric pressure
changes. After checking skimmed data created by DST production job,
the detector constants are improved on the weekly basis to correct for
this sort of effects. By getting updated constants, the re-processing
has been made for hadronic events.
Figure:
History of the event processing rate together with the data
acquisition rate.
|
In physics analyses, one does not need complete information available
in DST. Instead, easy access to experimental data is highly demanded
because we must play with a large amount of beam data at the
B-factory. For this purpose, minimal sets of DST (``mini-DST''), which
is compact but sufficient to study physics channels, are created for
all runs. The hadronic event size at this level is about 40 KB.



Next: Bibliography
Up: Offline Computing System
Previous: Level 4 Offline Trigger
Contents
Samo Stanic
2001-06-02
