


Next: Mechanical assembly
Up: Design and Construction of
Previous: Design and Construction of
Contents
The technical specifications for production of CsI(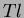 ) crystals are
required to meet a number of stringent optical and mechanical
requirements such as the average light output, light uniformity,
dimensions, and radiation hardness. The Budker Institute of Nuclear
Physics (BINP) in Novosibirsk, Russia with the collaboration of Single
Crystal Institute and Factory in Kharkov, Ukraine, Crismatec Co. in
France, and the Shanghai Institute of Ceramics (SIC) in China have
produced CsI(
) crystals are
required to meet a number of stringent optical and mechanical
requirements such as the average light output, light uniformity,
dimensions, and radiation hardness. The Budker Institute of Nuclear
Physics (BINP) in Novosibirsk, Russia with the collaboration of Single
Crystal Institute and Factory in Kharkov, Ukraine, Crismatec Co. in
France, and the Shanghai Institute of Ceramics (SIC) in China have
produced CsI(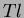 ) crystals to meet the Belle ECL specifications.
) crystals to meet the Belle ECL specifications.
Optical properties of each crystal were tested by irradiation with a
collimated  Cs source at nine points along the crystal and
measuring photoelectric peaks for 662 keV
Cs source at nine points along the crystal and
measuring photoelectric peaks for 662 keV 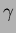 rays. Output
signals from a standard bialkali photomultiplier tube (Hamamatsu
R1847S) were shaped by an amplifier with a 1
rays. Output
signals from a standard bialkali photomultiplier tube (Hamamatsu
R1847S) were shaped by an amplifier with a 1 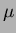 s shaping time and
digitized by a peak-sensing ADC. The nonuniformity of the light
collection is defined by the ratio of the difference between the
largest and smallest photo-peak values among the nine measurements to
the average photo-peak value. The nonuniformity is required to be less
than 9 % for all crystals and less than 7 % for 90 % of total
crystals.
s shaping time and
digitized by a peak-sensing ADC. The nonuniformity of the light
collection is defined by the ratio of the difference between the
largest and smallest photo-peak values among the nine measurements to
the average photo-peak value. The nonuniformity is required to be less
than 9 % for all crystals and less than 7 % for 90 % of total
crystals.
Measurements of the crystal dimensions were done with an automated
device with eight linear gauges. The system has a 20 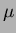 m precision
for unwrapped crystals. The lateral dimensions are required to be +0
and
m precision
for unwrapped crystals. The lateral dimensions are required to be +0
and  200
200 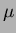 m from the specified dimensions and the length to be
m from the specified dimensions and the length to be
 1 mm from the specified length.
1 mm from the specified length.



Next: Mechanical assembly
Up: Design and Construction of
Previous: Design and Construction of
Contents
Samo Stanic
2001-06-02