


Next: Glass Resistive Plate Counters
Up: and Muon Detection System,
Previous: and Muon Detection System,
Contents
Figure ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) shows the Belle detector with the segmented
magnetic flux return iron in the barrel and end-cap regions. KLM
consists of alternating layers of charged particle detectors and 4.7
cm-thick iron plates. There are 15 detector layers and 14 iron layers
in the octagonal barrel region and 14 detector layers in each of the
forward and backward end-caps. The iron plates provide a total of 3.9
interaction lengths of material for a particle traveling normal to
the detector planes. In addition, the electromagnetic calorimeter,
ECL, provides another 0.8 interaction length of material to convert
shows the Belle detector with the segmented
magnetic flux return iron in the barrel and end-cap regions. KLM
consists of alternating layers of charged particle detectors and 4.7
cm-thick iron plates. There are 15 detector layers and 14 iron layers
in the octagonal barrel region and 14 detector layers in each of the
forward and backward end-caps. The iron plates provide a total of 3.9
interaction lengths of material for a particle traveling normal to
the detector planes. In addition, the electromagnetic calorimeter,
ECL, provides another 0.8 interaction length of material to convert
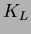 's.
's. 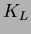 that interacts in the iron or ECL produces a shower of
ionizing particles. The location of this shower determines the
direction of
that interacts in the iron or ECL produces a shower of
ionizing particles. The location of this shower determines the
direction of 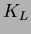 , but fluctuations in the size of the shower do not
allow a useful measurement of the
, but fluctuations in the size of the shower do not
allow a useful measurement of the 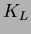 energy. The multiple layers of
charged particle detectors and iron allow the discrimination between
muons and charged hadrons (
energy. The multiple layers of
charged particle detectors and iron allow the discrimination between
muons and charged hadrons (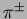 or
or 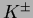 ) based upon their
range and transverse scattering. Muons travel much farther with
smaller deflections on average than strongly interacting hadrons.
) based upon their
range and transverse scattering. Muons travel much farther with
smaller deflections on average than strongly interacting hadrons.
Subsections



Next: Glass Resistive Plate Counters
Up: and Muon Detection System,
Previous: and Muon Detection System,
Contents
Samo Stanic
2001-06-02