


Next: Production of hydrophobic silica
Up: Aerogel Cerenkov Counter System,
Previous: Aerogel Cerenkov Counter System,
Contents
The configuration of the silica aerogel Cerenkov counter system,
ACC, in the central part of the Belle detector is shown in
Fig. ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) [42,43].
ACC consists of 960 counter modules segmented into 60 cells in the
[42,43].
ACC consists of 960 counter modules segmented into 60 cells in the
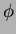 direction for the barrel part and 228 modules arranged in 5
concentric layers for the forward end-cap part of the detector. All
the counters are arranged in a semi-tower geometry, pointing to the
interaction point. In order to obtain good pion/kaon separation for
the whole kinematical range, the refractive indices of aerogels are
selected to be between 1.01 and 1.03, depending on their polar angle
region. A typical single ACC module is shown in
Figs.
direction for the barrel part and 228 modules arranged in 5
concentric layers for the forward end-cap part of the detector. All
the counters are arranged in a semi-tower geometry, pointing to the
interaction point. In order to obtain good pion/kaon separation for
the whole kinematical range, the refractive indices of aerogels are
selected to be between 1.01 and 1.03, depending on their polar angle
region. A typical single ACC module is shown in
Figs. ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) (a) and (b) for the barrel and the end-cap
ACC, respectively. Five aerogel tiles are stacked in a thin (0.2 mm
thick) aluminum box of approximate dimensions
(a) and (b) for the barrel and the end-cap
ACC, respectively. Five aerogel tiles are stacked in a thin (0.2 mm
thick) aluminum box of approximate dimensions
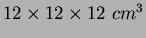 . In order to detect Cerenkov lights effectively, one or
two fine mesh-type photomultiplier tubes (FM-PMTs), which are
operated in a magnetic field of 1.5 T [44], are
attached directly to the aerogels at the sides of the box. We use PMTs
of three different diameters: 3 in. (R6683), 2.5 in. (R6682), and 2
in. (R6681) of Hamamatsu Photonics, depending on refractive indices,
in order to get uniform response for light velocity particles.
. In order to detect Cerenkov lights effectively, one or
two fine mesh-type photomultiplier tubes (FM-PMTs), which are
operated in a magnetic field of 1.5 T [44], are
attached directly to the aerogels at the sides of the box. We use PMTs
of three different diameters: 3 in. (R6683), 2.5 in. (R6682), and 2
in. (R6681) of Hamamatsu Photonics, depending on refractive indices,
in order to get uniform response for light velocity particles.
Figure:
The arrangement of ACC at the central part of the Belle detector.
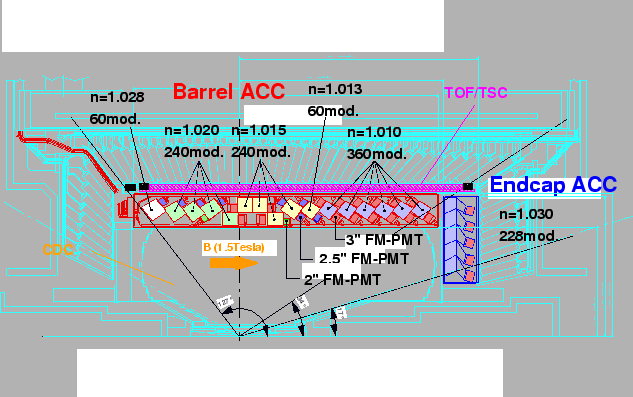 |
Figure:
Schematic drawing of a typical ACC counter module: (a) barrel
and (b) end-cap ACC.
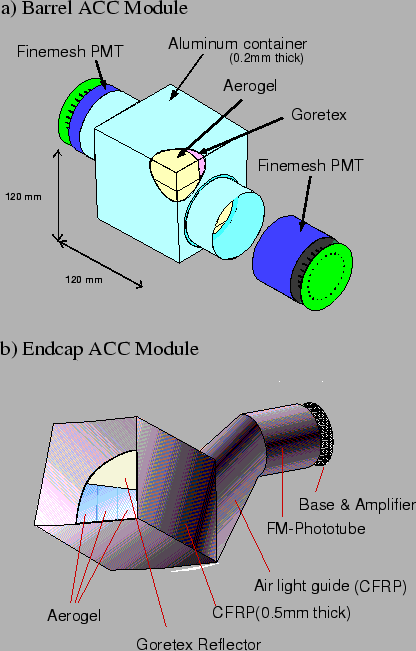 |
Subsections



Next: Production of hydrophobic silica
Up: Aerogel Cerenkov Counter System,
Previous: Aerogel Cerenkov Counter System,
Contents
Samo Stanic
2001-06-02
