


Next: Fine-mesh photomultiplier tubes
Up: Detector Design
Previous: Production of hydrophobic silica
Contents
All the aerogel tiles thus produced have been checked for optical
transparency, transmittance of unscattered light, refractive index,
dimension, etc.
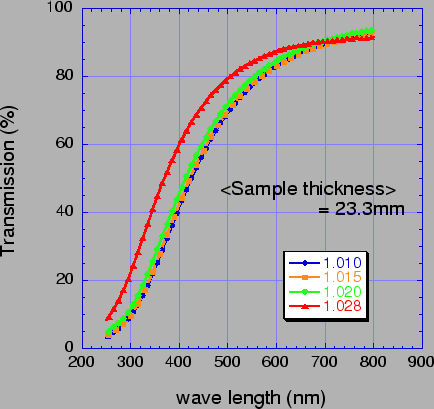
Fig. ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) shows typical transmittance curves
obtained by a photo-spectrometer for aerogels of four different
refractive indices. The
shows typical transmittance curves
obtained by a photo-spectrometer for aerogels of four different
refractive indices. The 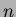 = 1.028 aerogels have better transmittance
than the others. Their average transmission length (
= 1.028 aerogels have better transmittance
than the others. Their average transmission length (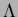 ) at 400
nm is 46 mm, while the others are around 25 mm. Here
) at 400
nm is 46 mm, while the others are around 25 mm. Here 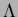 is
defined by the function:
is
defined by the function:
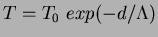 , where
, where 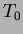 and
and
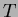 are the incident and transmitted light intensities, respectively,
and d is the thickness of an aerogel tile. These aerogels were
produced from the alcogel which was prepared by using methyl alcohol
as a solution.
are the incident and transmitted light intensities, respectively,
and d is the thickness of an aerogel tile. These aerogels were
produced from the alcogel which was prepared by using methyl alcohol
as a solution.
Figure:
Light transmittance spectra for silica aerogels (thickness =
23.3 mm) of 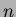 = 1.01, 1.015, 1.02 and 1.028. The silica aerogels of
= 1.01, 1.015, 1.02 and 1.028. The silica aerogels of
 = 1.028 prepared by using methanol as the preparation solvent
shows the best transmittance data.
= 1.028 prepared by using methanol as the preparation solvent
shows the best transmittance data.
 |
The refractive indices are well controlled as
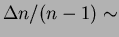 3% for all the produced aerogel tiles, which is essentially the same
as the measurement error of the refractive index determined by
measuring a deflection angle of laser light (He-Ne: 543.5 nm) at a
corner of each aerogel tile.
3% for all the produced aerogel tiles, which is essentially the same
as the measurement error of the refractive index determined by
measuring a deflection angle of laser light (He-Ne: 543.5 nm) at a
corner of each aerogel tile.
We carried out a test to ensure the radiation hardness of aerogels by
placing aerogel samples ( = 1.012, 1.018 and 1.028) in
high-intensity
= 1.012, 1.018 and 1.028) in
high-intensity 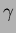 -rays from a
-rays from a  Co
source [48]. Transparencies and refractive indices of
aerogels were measured up to 9.8 Mrad, which corresponds to more than
10 years of running at KEKB. Neither deterioration on the
transparency nor change in the refractive indices were observed within
the errors of measurements after the irradiation. Measurement
accuracies were 0.8 % for the transparency and
Co
source [48]. Transparencies and refractive indices of
aerogels were measured up to 9.8 Mrad, which corresponds to more than
10 years of running at KEKB. Neither deterioration on the
transparency nor change in the refractive indices were observed within
the errors of measurements after the irradiation. Measurement
accuracies were 0.8 % for the transparency and  0.0006 for the
refractive index. Deterioration in transparency and changes of
refractive index after 9.8 Mrad
0.0006 for the
refractive index. Deterioration in transparency and changes of
refractive index after 9.8 Mrad 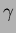 -ray irradiation were observed
to be less than 1.3% and 0.001 at 90% confidence level,
respectively.
-ray irradiation were observed
to be less than 1.3% and 0.001 at 90% confidence level,
respectively.



Next: Fine-mesh photomultiplier tubes
Up: Detector Design
Previous: Production of hydrophobic silica
Contents
Samo Stanic
2001-06-02

