The Belle detector was designed and constructed to carry out
quantitative studies of rare
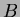
-meson decay modes with very small
branching fractions using an asymmetric e

e

collider operating
at the
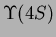
resonance, the KEK-B-factory. Such studies
require data samples containing
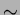
10
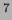
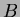
-meson decays. The
Belle detector is configured around a 1.5 T superconducting solenoid
and iron structure surrounding the KEK-B beams at the Tsukuba
interaction region.
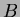
-meson decay vertices are measured by a silicon
vertex detector (SVD) situated just outside of a cylindrical beryllium
beam pipe. Charged particle tracking is performed by a wire drift
chamber (CDC). Particle identification is provided by
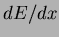
measurements in CDC, aerogel threshold Cerenkov counter (ACC)
and time-of-flight counter (TOF) placed radially outside of
CDC. Electromagnetic showers are detected in an array of CsI(
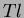
)
crystals (ECL) located inside the solenoid coil. Muons and
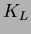
mesons are identified by arrays of resistive plate counters
interspersed in the iron yoke (KLM). The detector covers the
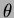
region extending from 17

to 150

. The part of the uncovered
small-angle region is instrumented with a pair of BGO crystal arrays
(EFC) placed on the surfaces of the QCS cryostats in the forward and
backward directions. Details of the design and development works of
the detector subsystems, which include trigger, data acquisition and
commputer systems, are described. Results of performance of the
detector subsystems are also presented.
